Neodymium magnets, also known as Neodym Magnet, are extremely powerful due to their unique composition and high energy density. The grades, such as N35-N52, indicate the amount of energy these magnets can store, which directly impacts their performance in demanding applications. The table below highlights the main differences among these grades:
Grade | Max Temp (°C) | Relative Cost | Key Distinctions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
N35 | 35 | 80 | $1.00 | Suitable for most uses, handles higher temperatures, more affordable |
N42 | 42 | 80–180 | $1.25 | 20% stronger than N35, better heat resistance |
N52 | 52 | 80 | $2.10 | 48% stronger than N35, compact size, more sensitive to heat |
Custom neodymium magnets (Customized Neodymium Magnet) are widely used across various industries, including electronics and renewable energy. These Neodymium Magnet can deliver a pull force of up to 6 kg, with a surface field strength ranging from 11,700 to 14,500 Gauss. N35-N52 magnets are now essential components in electric vehicles, wind turbines, and advanced medical devices. If you need specific shapes or strengths, Customized Neodymium Magnet can be tailored to meet your requirements.
Key Takeaways
Neodymium magnets have grades from N35 to N52. Higher numbers mean the magnets are stronger and hold more energy.
N35 magnets are cheaper and work well in hot or tough places. N52 magnets are the strongest but cost more and need careful use.
Custom neodymium magnets can be made in many shapes and sizes. They can have special coatings to stop rust and damage. This helps them fit different jobs in many industries.
Picking the right magnet grade depends on how strong it needs to be. You also need to think about heat, size, and cost. This helps get the best results and saves money.
Careful checks and good materials make sure custom magnets are high quality. This is important for electronics, medical tools, electric cars, and other uses.
Neodym Magnet Grades Explained

N35-N52 Meaning
Neodymium magnets, also called Neodym Magnet, use grades to show how strong they are. The grade, like N35 or N52, tells us the magnet’s Maximum Energy Product (BHmax). This is measured in Mega-Gauss-Oersteds (MGOe). The value comes from a special curve called the hysteresis curve. It is where the magnetic flux density (B) and field strength (H) are at their highest together. A bigger grade number means a stronger magnet. For example, N42 magnets have a BHmax of 42 MGOe. This system helps people pick the right magnet for their job.
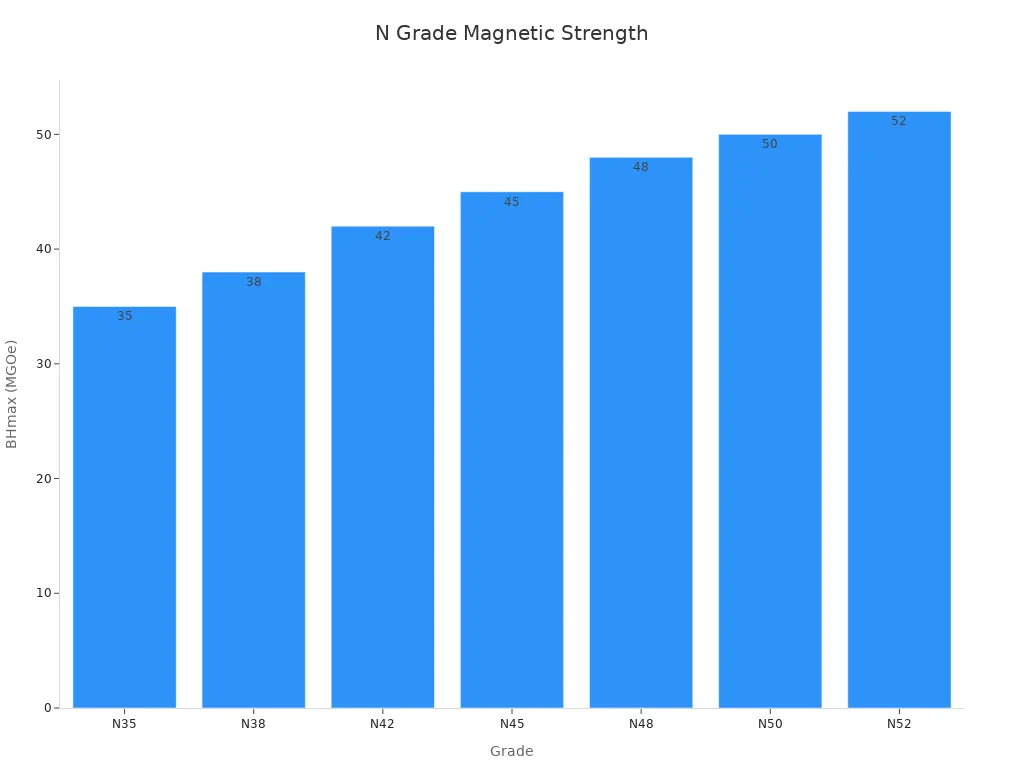
Grade | Maximum Energy Product (BHmax, MGOe) | Residual Induction (Br, kG) | Coercive Force (Hc, kOe) | Intrinsic Coercive Force (Hci, kOe) | Max Operating Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
N35 | 35 | 11.7 – 12.1 | 10.5 – 11 | 12 | 80 |
N38 | 38 | 12.2 – 12.6 | 11 – 11.5 | 12 | 80 |
N42 | 42 | 13.0 – 13.4 | 11.5 – 12 | 11 | 80 |
N45 | 45 | 13.5 – 13.8 | 11.5 – 12 | 11 | 80 |
N48 | 48 | 13.8 – 14.2 | 11.5 – 12 | 11 | 80 |
N50 | 50 | 14.3 – 14.6 | 11 – 11.5 | 11 | 80 |
N52 | 52 | 14.6 – 14.8 | 10.5 – 11 | 10 | 80 |
The ‘N’ in each grade stands for the maximum energy product. This is the main thing that shows how strong the magnet is.
Magnetic Strength
The strength of Neodym Magnet depends on its grade. When the grade number goes up from N35 to N52, both remanence (Br) and maximum energy product (BHmax) get higher. This means stronger magnets make stronger magnetic fields. For example, N35 magnets have a remanence of about 1.17 to 1.22 Tesla. N52 magnets can reach up to 1.47 Tesla. Stronger magnets let engineers use smaller magnets for the same job.
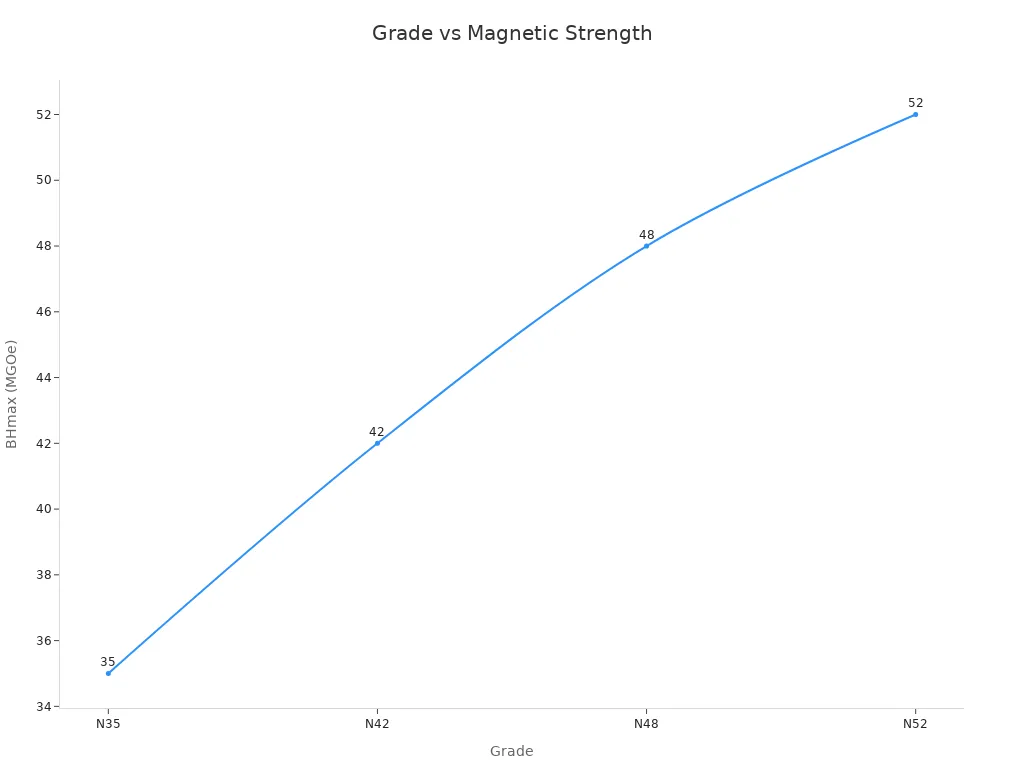
The number in the grade, like N35 or N52, shows the maximum energy product (BHmax).
Higher grades such as N45 to N52 give more magnetic strength and are good for tough jobs, like in cars or green energy.
Lower grades like N35 to N42 cost less and work well for things like electronics.
All standard grades can work up to 80°C.
Performance Factors
Many things affect how N35-N52 neodymium magnets work. The most important ones are:
Maximum Energy Product (BHmax): This tells how much magnetic energy the magnet can hold. A higher BHmax means a stronger magnet.
Residual Induction (Br): This shows the magnetic field left after the magnet is fully charged. A higher Br means a stronger field.
Coercive Force (Hc and Hci): These show how well the magnet keeps its strength. Stronger coercivity means it does not lose power easily.
Temperature Stability: All standard grades work up to 80°C. If it gets hotter, the magnet might get weaker or lose its magnetism.
Size and Shape: The size and shape of the magnet change how strong it is. Customized Neodymium Magnet can be made in many shapes for different uses.
N52 magnets are the strongest of the common grades. They are used when space and weight are important. But they cost more than lower grades like N35. When picking between N35-N52, people need to think about both strength and price. Customized Neodymium Magnet let you choose the grade, size, and shape you need.
N35 vs N52 Comparison
Strength Differences
N35 and N52 magnets are not the same in power or toughness. N52 magnets have the highest magnetic energy product, up to 52 MGOe. N35 magnets have about 35 MGOe. This means N52 magnets make much stronger magnetic fields and pull harder for the same size. The table below shows the main technical differences:
Parameter | N35 Magnet | N52 Magnet |
|---|---|---|
Magnetic Energy Product (BHmax) | ~35 MGOe | ~52 MGOe |
Remanence (Br) | ~1.17 Tesla | ~1.48 Tesla |
Coercivity (Hc) | ~868 kA/m | ~827 kA/m |
Max Operating Temperature | 80°C |
N52 magnets give about 48% more magnetic energy than N35. But N35 magnets work better at higher temperatures and do not lose their magnetism as easily. N52 magnets can break more easily and need gentle handling.
Cost and Value
N52 magnets cost a lot more than N35 magnets. The price can be 70% to 100% higher for N52. This is because they use more neodymium and need careful making. N52 magnets also need special cutting, which makes them about 23% more expensive to produce.
N52 magnets give up to 49% more magnetic energy for their size.
N35 magnets are a better deal for most uses, especially if you do not need super strong magnets.
N35 magnets last longer in places with lots of shaking or heat.
N52 magnets are worth the price when you need the strongest magnet in a small space.
Picking the right grade means thinking about how strong you need the magnet, how much you want to spend, and how tough it needs to be.
Typical Uses
N35 magnets are good for jobs that need medium strength, toughness, and low cost. People use them in car parts, building tools, magnetic name tags, and storage tools. N35 magnets also work better in wet or hot places. They keep up to 92% of their magnetism after five years.
N52 magnets are best for high-tech and small-space jobs. Engineers use them in electric motors, medical machines, MagSafe gadgets, and airplane parts. Their small size and strong pull make them great for fancy electronics and exact tools, but they do not like heat or wetness.
Attribute | N35 Magnets | N52 Magnets |
|---|---|---|
Moderate (35 MGOe) | Highest (52 MGOe) | |
Temperature Limit | Up to 120°C (special grades) | |
Cost Efficiency | High | Lower |
Common Applications | Tools, machinery, outdoor equipment | Motors, medical devices, electronics |
Durability | Excellent in harsh environments | More prone to demagnetization |
N35 magnets are best when you want something reliable and not too expensive. N52 magnets are best when you need the strongest magnet in a small space.
Customized Neodymium Magnet

Making custom neodymium magnets takes many careful steps. Each step helps make sure the Neodym Magnet works well for different jobs. The process includes picking the right material and grade, choosing the shape and size, adding coatings, and checking quality. Every part is important to make strong Customized Neodymium Magnet for things like electronics and green energy.
Material and Grade Selection
Choosing the best material and grade is the first step. Makers start with very pure neodymium, iron, and boron. Sometimes they add cobalt or dysprosium to help with heat and strength. The grade, like N35 or N52, depends on how strong the magnet needs to be and where it will be used. Some grades, like N42SH or N52H, can handle more heat.
Use raw materials that are more than 99.9% pure.
Melt and mix them in special ovens hotter than 1500°C.
Crush and grind the mix into a fine powder safely.
Press the powder into molds with strong magnets to line up the pieces.
Heat and treat the shapes to make them stronger.
Cut and shape the magnets to the right size.
Add coatings to stop rust.
Magnetize the finished magnets in the right direction.
Check if the magnets are strong, the right size, and coated well.
Pack and send the magnets as customers want.
The grade always matches what the job needs for strength, heat, and toughness. Makers use charts and data to pick the best grade for the price.
Shape and Size Options
Customized Neodymium Magnet can be made in many shapes and sizes. New ways of making things, like 3D printing, let people design magnets that are not just simple shapes. This helps engineers fit magnets perfectly in their products.
Shape Type | Magnetization Type(s) | Size Range / Dimensions | Additional Features / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Disc / Cylinder | Axial | Diameter: 1mm–300mm; Thickness: 0.5mm–50mm+ | Good for sensors and small spaces |
Block / Rectangular | Axial, Radial, Thickness | Minimum: 1mm × 1mm × 1mm | Used in motors and circuits |
Arc / Segment | Radial | Arc precision ±0.1° | Common in motor parts and generators |
Custom Shapes | Custom directions | Machined to drawings | Can have holes, grooves, and special shapes |
Makers use wire cutting, grinding, and lasers to get the right size. They can also change the way the magnet pulls, like axial or radial, for special uses.
Coatings and Durability
Neodymium magnets can rust, so coatings are needed to keep them strong. The coating depends on where and how the magnet will be used. Common coatings are nickel, gold, zinc, epoxy, and rubber. Each one protects the magnet in a different way.
Coating Type | Corrosion Resistance | Durability & Impact Resistance | Special Properties & Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
Nickel (Ni-Cu-Ni) | Good in air, okay in wet places | Smooth, not easy to scratch | Most used, good price, found in motors and sensors |
Gold (Ni-Cu-Ni+Au) | Very good, safe for medical use | Thin, looks nice | Safe for the body, conducts electricity, costs more |
Zinc (Zn) | Not as good as nickel, needs extra care | Okay strength | Used when nickel is not good, looks blue |
Epoxy/Plastic | Great against water | Good at taking hits | Best for wet places, does not conduct electricity |
Rubber/Silicon | Grips well, waterproof | Great at taking hits | Used for grip, stops chipping |
Tests like salt spray and scratch checks show the right coating makes Neodymium Magnet last longer, even in tough places.
Quality Control
Strict checks make sure every Customized Neodymium Magnet is high quality. Makers use special plans and tools to watch every step. They test how strong the magnet is, if the size is right, and if the coating is good. They follow rules like ISO 9001 and IATF 16949.
Check raw materials for purity and mix.
Test magnet strength with special tools.
Measure size with machines.
Test coatings to see if they stick and stop rust.
Sort magnets and check which way they pull.
Give reports and certificates with each order.
These steps make sure N35-N52 magnets work well in all jobs, from medical tools to electric cars.
Choosing N35-N52 Magnets
Application Needs
Picking the right neodymium magnet grade starts with knowing what the job needs. Engineers look at how strong the magnet must be. They also check how hot it will get, how tough it should be, and what size and weight are best. The place where the magnet will work is important too. For example, a small but strong N52 magnet is good for a motor that needs to save space. A car sensor might use an N42 or N35 magnet because they cost less and last longer. The steps usually go like this: First, find out how strong the magnet must be and what temperatures it will face. Next, pick the material and grade, like N35 or N52, that fits those needs. Then, choose the shape and size so it fits in the device. After that, use computer tools to guess how the magnet will work. Finally, test the magnet in real life to make sure it works well.
Studies show that picking the right magnet grade for the job makes things work better and last longer. For example, N52 magnets are best for medical tools and science gear. N42 or N35 magnets are better for things like phones and car sensors.
Cost vs Performance
It is important to think about both price and power when choosing between N35 and N52 magnets. N52 magnets are about 40-50% stronger than N35 magnets. This makes them great for hard jobs, but they cost more and are harder to get. N35 magnets work well for less money and are easier to find. The table below shows how they compare:
Factor | N35 Magnet | N52 Magnet |
|---|---|---|
Magnetic Strength | ~35 MGOe | |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Durability | Similar | Similar |
Application Suitability | Basic needs | High-performance |
Size for Same Strength | Larger | Smaller |
People should pick the lowest grade that does the job to save money. For most uses, N35-N52 magnets give a good mix of strength, price, and how easy they are to get.
Knowing about neodymium magnet grades and how to customize them helps people pick the right magnet for each job. Different businesses need special magnets to make sure things work well and last long. The table below explains why making magnets to fit each job is important:
Segment Category | Details | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
Product Type | Sintered and Bonded magnets | Sintered magnets are about four times stronger than bonded ones. This shows why it is important to make and grade magnets for each use. |
End User | Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Medical Devices, Energy, General Industrial, Others | Many industries need different magnets. Custom magnets help things like electric cars and medical tools work their best. |
Magnet Type | NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) and SmCo (Samarium-Cobalt) | NdFeB magnets are used most because they are small, strong, and save energy. Picking the right magnet type for each job is very important. |
Choosing the best N35-N52 magnet means thinking about how strong it needs to be, what size it should have, and where it will be used. Companies like ZhaoBao follow strict rules to make good magnets and can make special ones if needed. People should talk to experts to get magnets that fit their needs and work well every time.
FAQ
What does the "N" in N35 or N52 stand for?
The “N” stands for neodymium. The number tells how strong the magnet is. A bigger number means a stronger magnet. For example, N52 is stronger than N35.
Can neodymium magnets lose their strength over time?
Neodymium magnets stay strong for many years. Heat, hard hits, or some chemicals can make them weaker. Good coatings and careful use help them last longer.
Are custom neodymium magnets safe for medical devices?
Medical neodymium magnets have special coatings like gold or epoxy. These coatings stop rust and keep people safe. Makers test these magnets to meet tough medical rules.
What shapes can custom neodymium magnets be made in?
Makers can make many shapes like discs, blocks, rings, arcs, and special forms. Engineers pick the best shape for each job. Custom shapes help magnets fit just right in devices.


1 Comment
[…] different magnets wear out at different speeds. Neodymium magnets lose strength faster in heat or moisture. Ferrite magnets last longer in tough conditions. Choose […]